What is solar Angles?
Why Is It Require:
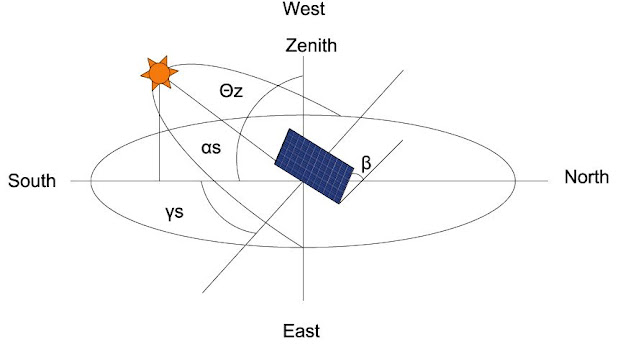
Zenith Angle, Θz: This is the angle between the line
that points to the sun and the vertical — basically, this is just where the sun
is in the sky. At sunrise and sunset this angle is 90º.
Solar Altitude
Angle, αs: This is the
angle between the line that points to the sun and the horizontal. It is the
complement of the zenith angle. At sunrise and sunset this angle is 0º.
Solar Azimuth
Angle, γs: This is the
angle between the line that points to the sun and south. Angles to the east are
negative. Angles to the west are positive. This angle is 0º at solar noon. It
is probably close to -90º at sunrise and 90º at sunset, depending on the
season. This angle is only measured in the horizontal plane; in other words, it
neglects the height of the sun.
Angle of
Incidence, θ: This is the
angle between the line that points to the sun and the angle that points
straight out of a PV panel (this is also called the line that is normal to the
surface of the panel). This is the most important angle. Solar panels are the
most efficient when pointing at the sun, so engineers want to minimize this
angle at all times. To know this angle, you must know all of the angles listed
and described next.
Hour Angle, ω: This is based on the sun's angular
displacement, east or west, of the local meridian (the line the local time zone
is based on). The earth rotates 15º per hour so at 11am, the hour angle is -15º
and at 1pm it is 15º.
Surface Azimuth
Angle, γ: This is the
angle between the line that points straight out of a PV panel and south. It is
only measured in the horizontal plane. Again, east is negative and west is
positive. If a panel pointed directly south, this angle would be 0º.
Collector
Slope, β: This is the
angle between the plane of the solar collector and the horizontal. If a panel
is lying flat, then it is 0º. As you tip it up, this angle increases. It does
not matter which direction the panel faces.
Declination, δ:
This is the
angle between the line that points to the sun from the equator and the line
that points straight out from the equator. North is positive
and south is negative. This angle varies from 23.45 to -23.45 throughout the
year, which is related to why we have seasons.
Latitude, φ: This is the angle between a line that
points from the center of the Earth to a location on the Earth's surface and a
line that points from the center of the Earth to the equator.
Tilt Angle:It is the angle between vertical earth surface and slope of PV panels.
Solar Noon: The time of day when the sun is the highest in the sky.







No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any span link in the comment box.